TB-9-2920-225-34-1 - Page 19 of 70
TB 9-2920-225-34-1
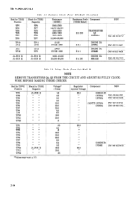
Table 2-4. Substitutes for D1-Model 03
If the regulator still does not function correctly
it will be necessary, if local skills permit, to test
each component. All the parts should be checked
with an ohmmeter and the capacitors checked with
a capacitance meter.
The circuit board traces
should be checked with an ohmmeter to make sure
that there are no cracked traces. Traces with hair-
line cracks will show good at lower temperatures
and will tend to show open circuit at higher tem-
peratures. If the board seems good at room tem-
perature, but the regulator still fails, this could
be the cause.
Section IV. VAP-AIR MODEL 26440001-04
2-8. General.
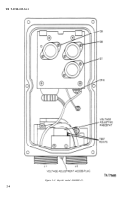
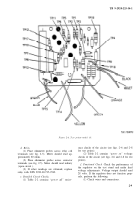
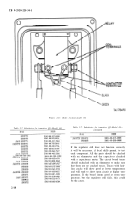
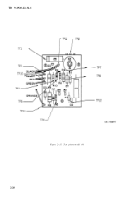
Figure 2-10 is a plan view of the
regulator with the cover off. Figure 2-11 is an
end view of the regulator showing the receptacles
and the voltage adjustment points. Figure 2–12 is
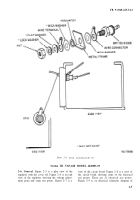
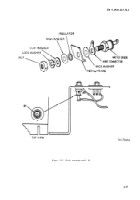
an exploded view of the diode mounting. Figure
2–13 is a relay location. Figure 2–14 is a view of
the circuit board and transistor heat sink. Figure
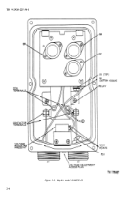
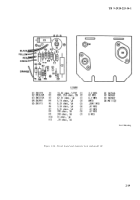
2–15 is a view of the circuit board showing the
electrical test points. There are 12 electrical test
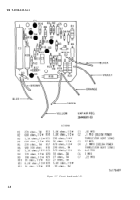
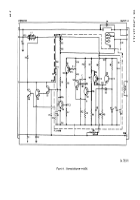
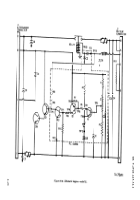
points. Figure 2–16 is an electrical schematic dia-
gram of the regulator. Table 2–5 lists the resist-
ance checks, and table 2-6 1ists the voltage checks.
Table 2–7 is a transistor substitution list.
2-9. Checkout and Repair.
a. Voltage Adjustment Rheostat (Rz) (Power
Disconnected).
(1) Place ohmmeter test probes to terminals
of the rheostat (see fig. 2-10).
(2) Rotate rheostat fully clockwise, reading
should be approximately 250 ohms.
(3) Rotate rheostat fully counterclockwise,
reading should be less than 5 ohms.
(4) If other readings are obtained, replace
rheostat.
b. Transistors.
(1) Remove transistors Q4 and Q5 (see fig.
2–l0).
(2) Position transistors as shown in figure
2-1, and check them separately (see fig. 2–2).
(3) If resistance values cliffer from the values
shown in figure 2–2, replace the transistors
through cannibalization or requisition transistor
Q4, Vap-Air part number 26316033-12 (2N3441),
NSN 5961–00–054–4141, or transistor Q5, Vap-
Air P N 26316033–70 (2N3773), NSN 5961–00–
929–5014 (see table 2–7 for substitutes).
(4) Check the mica insulating washers be-
tween the transistors and mounting plate. Replace
if cracked, broken or missing. Coat washers with
insulation compound per MIL–S–8660, NSN 6850–
00-880-7616.
c. Diode.
(1) Remove four screws holding transistor
and circiut board mounting plate, and move plate
to one side.
(2) Place negative ohmmeter probe to the
topside of diode D4 (see fig. 2-12).
(3) Place positive probe to the bottom of D4.
Meter should indicate low resistance.
(4) Reverse probes. Meter should indicate
high resistance.
(5) If other readings are obtained replace
diode D4 (MR1122), NSN 5961–00–103–1519 (see
fig. 2-12) .
d. Relay.
(1) Place ohmmeter probes across relay coil
terminals (see fig. 2-13).
(2) Place ohmmeter probes across terminals
(see fig. 2-13). Meter should read infinity (open
circuit).
(3) If other readings are obtained, replace
relay, NSN2920–00–735–9542.
(4) Reinstall transistor and circuit board
mounting plate.
e. Detailed Circuit Checks.
(1) Table 2–5 contains
“power off’’
resistance
checks of the circuit (see fig. 2–15 for test points).
(2) Table 2-6 contains
“power on”
voltage
checks of the circuit (see fig. 2–15 for test points).
f. Functional Check.
Check the performance of
the regulator on the test stand and make final volt-
age adjustments. Voltage output should read 28
volts. If the regulator does not function properly,
perform the following:
( 1 ) Check wires and connections.
2-13
Back to Top