TM-5-3805-254-14-P-2 - Page 287 of 894
ELECTRICAL
Section VV
TRUCK SERVICE MANUAL
Page 6
Test No.
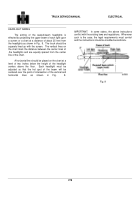
3 Voltage Drop Test
Generally, the starting or cranking circuit is a
series circuit from the battery insulated post to the
starting motor solenoid, to the motor, to ground (chassis)
and return to the battery ground post, Fig.
6.
In the cranking circuit we also have a cranking
control circuit, Fig.
6.
In this circuit the solenoid is
controlled or operated by closing an ignition switch or
push button starting switch at the instrument panel.
In
this cranking control circuit there are frequently some
safety switches such as transmission "neutral safety
switch" and/or vacuum operated cutout switch.
Fig.
6
Starting Motor Circuit
Excessive resistance in the starting or cranking
system circuit will cause slow cranking speeds and hard
starting.
The starting system will function properly only
when the "cranking circuit" and "control circuit" with the
components are in satisfactory condition.
Corrosion, loose terminal, damaged or undersized
cables (wires) will cause cranking problems.
In addition,
the switches involved must make good electrical
connections when closed.
The voltage drop test will be performed in three
steps: cranking circuit, control circuit and grounded side.
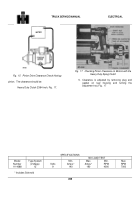
Cranking Circuit:
Voltage drops are measured by
connecting a voltmeter in parallel across the circuit or
section of a circuit being inspected, then reading the
voltmeter while circuit is in operation.
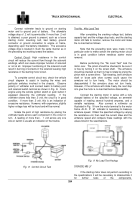
To test voltage
drop in the cranking circuit from battery to starter,
connect the voltmeter (observing the polarity and voltage
rating of meter) to battery post
CTS2259K
(not clamp) to starter motor terminal as shown in Fig.
7.
Prevent engine from starting during test.
Crank engine
and observe voltmeter reading.
Fig.
7
Cranking Circuit Test
Values of maximum voltage drops for a standard 12volt
cranking circuit are as follows:
Cable Under Three (3) Feet
.1
Cable Over Three (3)to Six (6) Feet
.2
Mechanical Switch
.1
Solenoid Switch
.2
Magnetic Switch
.3
Each Connection
.0
Add these values together.
For example, you have
a total of .5 volt and you have less than .
5 volt drop,
continue to grounded side test.
However, if you have more than .5 volt drop, you
have an excessive voltage drop. This must be located by
moving test lead from starting motor and working toward
the battery. Crank engine and each move.
When a
noticeable decrease in the voltage reading is obtained
the trouble will be located between that point and the
preceding point checked.
Items which could be at fault can either be a damaged
cable or poor connection, an undersized wire or possibly
a bad solenoid (contact within the solenoid).
Repair the
fault.
Grounded Side: High resistance in ground circuit of
starting motor system will result in hard starting and may
affect
the
charging
circuit
as
well.
283
Back to Top