TM-9-2350-256-34 - Page 23 of 584
TM 9-2350-256-34
0002 00
INTERMEDIATE MAINTENANCE
RECOVERY VEHICLE, FULL TRACKED: MEDIUM, M88A1
NSN 2350-00-122-6826, EIC AQA
DESCRIPTION AND DATA
EQUIPMENT CHARACTERISTICS, CAPABILITIES, AND FEATURES
Introduction
The Recovery Vehicle, Full Tracked: Medium, M88A1 is a medium-armored, full-track-laying, low-silhouette vehicle that
performs hoisting, winching, and towing operations for tanks and other vehicles. The vehicle also supports medium and light
tank units to effect battlefield recovery. Further detailed descriptions of the individual assemblies and components covered for
replacement and/or repair in this manual will be found in pertinent WPs. General operating and maintenance descriptions are
found in TM 9-2350-256-10 and TM 9-2350-256-20.
LOCATION AND DESCRIPTIONS OF MAJOR COMPONENTS
General
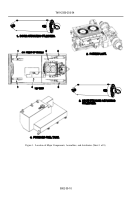
The general location of major components, assemblies, and auxiliaries is shown on Figure 1.
Powerplant
The powerplant is composed of the Continental Model AVDS-1790-2DR air-cooled, 12-cylinder, diesel engine and the Allison
(GM) Model XT-1410-4 cross-drive transmission. The powerplant is removed and installed as a unit. Separation of engine
from transmission center section is performed after the powerplant has been removed from the vehicle. The powerplant supplies
electrical power through a generator and motive power through the output reduction units.
Fuel System
The fuel system includes liquid fuel (diesel) storage and delivery system. Fuel storage consists of three separate fuel tanks. Fuel
is fed to the engine by an electric pump through a system of hoses and valves. Fuel is strained at the tank filler openings as the
tanks are filled, and filtered through separate and renewable filter elements as it is fed to the engine. Combustion air is cleaned
by two air cleaners and driven into the engine intake manifolds by two turbosuperchargers.
Fuel Tanks
All tanks are of a welded steel construction. The left rear tank contains the filler cap and filter assembly. Fuel level sending units
are contained within the right rear and forward tanks. An electric fuel pump is located in the forward fuel tank sump cavity,
allowing complete drainage of the tank before tank removal. All tanks are interconnected and shock mounted. Grounding straps
are provided to ensure discharge of any static electricity which might accumulate.
Fuel Pump
The electric fuel pump located in the forward fuel tank sump cavity is a centrifugal pusher-type pump designed for submerged
operation. It is hermetically sealed and contains a 24-volt dc motor to operate the pump. A strainer is provided as an integral
part of the pump assembly for efficient fuel filtering. The fuel pump is shock mounted in a support assembly which suspends the
pump in the fuel tank and also provides a housing for fuel and electrical connections.
Purge Pump
The purge pump handle is located on the floor to the left of the driver’s position. The purge pump is used to pump air from the
fuel lines and to facilitate engine starting in cold weather.
Main Engine Generator System
During periods of main engine operation, the vehicle electrical system derives its power from a 300-ampere, 28-volt dc generator
and is driven by the main engine. This generator also serves to charge the vehicle batteries during periods of main engine
operation. The vehicle battery system, consists of six 12-volt, 100-ampere-hour batteries connected in a series-parallel to
supply 24-volts dc to the electrical system when the generator is not running. A solid state voltage regulator serves to maintain
a constant generator output voltage of 28 ± 0.7 volts dc when the generator is powering the electrical system and charging
0002 00-1
Back to Top