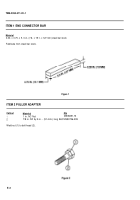
TM-9-2350-311-20-1 - Page 1161 of 1275
F-3 TIGHTENING METAL FASTENERS
When torquing a fastener, select a torque wrench whose range (Table F-2) fits the required torque value. A torque
wrench is most accurate from 25% to 75% of its stated range. A torque wrench with a stated range of 0-100 Ib-ft (0-1 36
N.m) will be most accurate from 25-75 lb-ft (34-102 N-m). Accuracy of readings will decrease as you approach 0 Ib-ft
(0 N·m) or 100 lb-ft (136 N·m). The following ranges (Table F-2) are based on this principle.
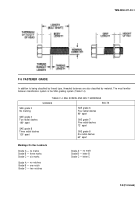
TABLE F-2 TORQUE RANGES
STATED RANGE
MOST EFFECTIVE RANGE
F-4 FASTENER SIZE AND THREAD PATTERN
Threaded fasteners are categorized according to diameter of fastener shank. Thread styles are divided into broad
groups, the two most common ranges being coarse (Unified Coarse-UNC) and fine (Unified Fine-UNF). These groups
are defined by the number of threads per in. on the bolt shanks. In addition, threads are categorized by thread class
(Table F-3), which is a measure of the degree of fit between the threads of the bolt or screw (external threads) and the
threads of the attaching nut or tapped hole (internal threads). The most common thread class for bolts and screws is
class 2.
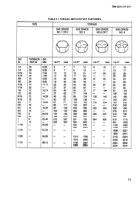
TABLE F-3 THREAD CLASSES AND DESCRIPTION
EXTERNAL
INTERNAL
FIT
1A
1B
Loose fit
2A
2B
Medium fit
3A
3B
Close fit
Thread patterns are designed as follows:
NOTE
Unless followed with -LH (e.g., 3/4-1 OUNC-2A-LH), threads are right-hand.
TM9-2350-311-20-1
F- 4
Back to Top