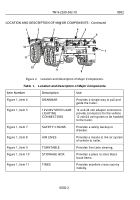
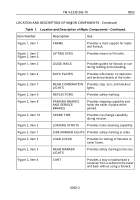
TM-9-2330-342-10 - Page 48 of 500
CORROSION PREVENTION AND CONTROL (CPC) - Continued
salts. An example is the rusting of iron. Corrosion damage in metals can be seen, depending
on the metal, as tarnishing, pitting, fogging, surface residue, and/or cracking.
Plastics, composites, and rubbers can also degrade. Degradation is caused by thermal
(heat), oxidation (oxygen), solvation (solvents), or photolytic (light, typically UV) processes.
The most common exposures are excessive heat or light. Damage from these processes
will appear as cracking, softening, swelling, and/or breaking.
SF Form 368, Product Quality Deficiency Report should be submitted to the address
specified in DA PAM 750-8, The Army Maintenance Management System (TAMMS) Users
Manual.
DESTRUCTION OF ARMY MATERIEL TO PREVENT ENEMY USE
Command decision, according to the tactical situation, will determine when the destruction
of the equipment will be accomplished. A destruction plan will be prepared by the using
organization unless one has been prepared by a higher authority. Refer to TM 750-244-6,
Procedures for Destruction of Tank Automotive Equipment to Prevent Enemy Use, for
general destruction procedures.
PREPARATION FOR STORAGE OR SHIPMENT
For detailed information on preparing the PLST M1076 A1 for storage or shipment refer to
WARRANTY INFORMATION
The PLST M1076 A1 is warranted for 12 months. The warranty starts on the date found in
block 23 of DA Form 2408-9, Equipment Control Record. Report all defects to your
supervisor, who will take appropriate action.
NOMENCLATURE CROSS-REFERENCE LIST
Table
1.
Nomenclature Cross-Reference List.
Common Name
Official Nomenclature
Gladhand
Quick disconnect air coupling
Service Brake Pedal
Brake pedal
Throttle Pedal
Throttle control
Towing Eye
Drawbar lunette
TM 9-2330-342-10
0001
0001-2
Back to Top