TM-9-2350-311-20-2 - Page 749 of 828
TM 9--2350--311--20--2
Change 4
B--1
APPENDIX B
MAINTENANCE ALLOCATION CHART (MAC)
SECTION I. Introduction
B--1
THE ARMY MAINTENANCE SYSTEM MAC
a. This introduction (Section I) provides a general explanation of all maintenance and repair functions authorized at two
maintenance levels under the two level Army Maintenance System concept.
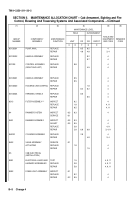
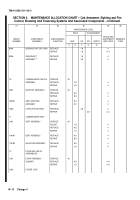
b. The Maintenance Allocation Chart (MAC) in Section II designates overall authority and responsibility for the perform-
ance of maintenance functions on the identified end item or component. The application of the maintenance functions
to the end item or component will be consistent with the capacities and capabilities of the designated maintenance
levels, which are shown in the MAC in column (4) as:
Field
-- includes two subcolumns, unit and direct support maintenance.
Unit
-- includes two subcolumns, C (operator/crew) and O (unit) maintenance.
Direct Support
-- includes an F subcolumn.
Sustainment
-- includes two subcolumns, general support and depot maintenance.
General Support
-- includes an H subcolumn.
Depot
-- includes a D subcolumn.
c.
Section III lists the tools and test equipment (both special tools and common tool sets) required for each maintenance
function as referenced from Section II.
d. Section IV contains supplemental instructions and explanatory notes for a particular maintenance function.
B--2
MAINTENANCE FUNCTIONS
Maintenance functions are limited to and defined as follows:
a. Inspect.Todeterminetheserviceabilityofanitembycomparingitsphysical,mechanical,and/orelectricalcharacteris-
tics with established standards through examination (e.g. by sight, sound, or feel).
b. Test.Toverifyserviceabilitybymeasuringthemechanical,pneumatic,hydraulic,orelectricalcharacteristicsofanitem
and comparing those characteristics with prescribed standards.
c.
Service. Operations required periodically to keep an item in proper operating condition, e.g., to clean (includes decon-
taminate, when required), to preserve, to drain, to paint, or to replenish fuel, lubricants, chemical fluids, or gases.
d. Adjust. To maintain or regulate, within prescribed limits, by bringing into proper position, or by setting the operating
characteristics to specified parameters.
e. Align. To adjust specified variable elements of an item to bring about optimum or desired performance.
f.
Calibrate. To determine and cause corrections to be made or to be adjusted on instruments or test, measuring, and
diagnostic equipment used in precision measurement. Consists of comparisons of two instruments, one of which is a
certified standard of known accuracy, to detect and adjust any discrepancy in the accuracy of the instrument being
compared.
Back to Top