TM-9-2990-205-34-P - Page 11 of 128
TM 9--2990--205--34&P
0001 00--1
GENERAL INFORMATION
0001 00
THIS WORK PACKAGE COVERS:
General Information
SCOPE
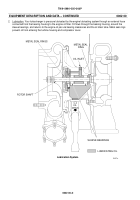
Type of Manual: This technical manual contains instructions for maintenance and repair of the Model 5HDR
Turbosupercharger at the Direct and General Support levels.
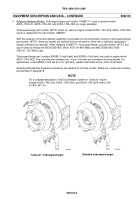
Equipment Identification: There are four configurations of Model 5HDR turbosupercharger covered in this manu-
al. Part numbers 11668377--1 (standard, no longer available) and 187727 (clean air) can be mounted on either
the right or left bank of various AVDS--1790 series engines. Part numbers 655595--3 (right bank) and 655595--4
(left bank) are used on AVDS--1790--8CR engines.
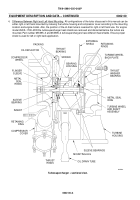
Purpose of the Equipment: Turbosuperchargers are basically centrifugal blowers driven by engine exhaust gases
which deliver high volumes of compressed air to the engine intake manifold. Engines with turbosuperchargers are
able to develop more power per unit of fuel consumed.
MAINTENANCE FORMS, RECORDS AND REPORTS
Department of the Army forms and records used for equipment maintenance will be those prescribed by DA PAM
750--8, the Army Maintenance Management System (TAMMS) Operators Manual.
CORROSION PREVENTION AND CONTROL
Corrosion Prevention and Control (CPC) or Army materiel is a continuing concern It is important that any corro-
sion problem with the turbocharger be reported so that improvements can be made to prevent the problem in the
future. While corrosion is typically associated with rusting of metals, it can also include deterioration of other ma-
terials such as rubber and plastic. Unusual cracking, softening, swelling, or breaking of these materials may be a
corrosion problem. If a corrosion problem is identified, it can be reported using SF 368, (Product Quality Deficien-
cy Report). Use of keywords such as “corrosion”, “rust”, deterioration”, or “cracking” will ensure that the informa-
tion is identified as a CPC problem. SF 368 should be submitted to the address specified in DA PAM 750--8.
DESTRUCTION OF ARMY MATERIEL TO PREVENT ENEMY USE
Refer to TM 750--244--6 for procedures on how to destroy the starter.
Below are some general guidelines to follow in destruction of equipment to prevent enemy use.
Destruction of equipment, when subject to capture or abandonment in a combat zone, will be undertaken only
when such action is necessary in accordance with orders of, or policy established by the Army commander.
In general, destruction of essential parts, followed by burning, will usually be sufficient to render equipment use-
less. Time is usually critical.
Material must be damaged so that it cannot be restored to usable condition by either repair or cannibalization. If
lack of time or personnel prevents destruction of all parts, give priority to destruction of parts hardest to replace. It
is important that the same parts be destroyed on all starters to prevent construction of one complete starter from
several damaged ones.
PREPARATION FOR STORAGE OF EQUIPMENT
Instructions for preservation administrative storage of your turbosupercharger are contained in WP 0012 00.
QUALITY OF MATERIAL
Material used for replacement, repair, or modification must meet the requirements of this manual. If quality of ma-
terial requirements are not stated in this manual, the material must meet the requirements of the drawings, stan-
dards, specifications, or approved engineering change proposals applicable to the subject equipment.
Back to Top