TM-1-1500-344-23-2 - Page 149 of 240
8-5
NAVAIR 01-1A-509-2
TM 1-1500-344-23-2
15 April 2009
NOTE
Current formulation of MIL-L-87177 Grade B
contains Halon 141B, which may be subject to
environmental restrictions in some locations.
8-6.6. MIL-L-87177 (LUBRICANTS, CORROSION
PREVENTIVE COMPOUND, WATER DISPLACING,
SYNTHETIC). MIL-L-87177 Grade B is a synthetic
lubricant with added corrosion inhibitor. This material
creates a non-tacky film on the surface. MIL-L-87177
does not displace water or penetrate as thoroughly as
MIL-PRF-81309 or MIL-PRF-32033 and should only be
used on surfaces that have been wiped dry. Tight
crevice locations should have a coating of
MIL-PRF-81309 applied prior to use of MIL-L-87177 to
ensure proper protection.
CAUTION
Do not use corrosion preventive compounds on
the interior of fuel tanks or fuel cells, engines, or
engine fuel systems.
Do not use corrosion preventive compounds on
engine parts or accessories which exceed 800
°
F
(427
°
C). Hot corrosion reactions may occur.
CPCs are not compatible with liquid oxygen
and should not be used on oxygen equipment,
lines, fittings or storage bottles.
NOTE
Use only corrosion preventive compounds
(CPCs) authorized by the parent service
organization and described in this manual.
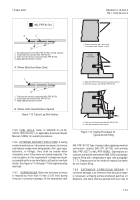
8-7. PRESERVATION OF SPECIFIC AREAS
.
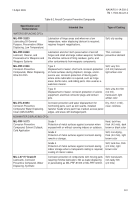
Table 8-3 provides procedures for the preservation of
specific areas and components where the use of a CPC
on exposed metal surfaces is generally recommended
for reducing corrosion. This list does not constitute
authority to use CPCs on specific equipment. The use
of some or all types of CPCs in certain areas or on
equipment may be detrimental. Therefore, consult the
appropriate corrosion and maintenance manuals before
applying a CPC in a new area and determine which, if
any, compounds should be used in that area. If
application of a CPC is required, and no specific
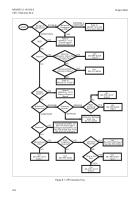
instructions are available, the CPC Decision Tree
(Figure 8-1) may be used as a guideline to determine
the most appropriate CPC.
WARNING
CPCs and solvents can produce toxic vapors.
Use only in well ventilated areas. Avoid contact
with skin. Consult local safety office for personal
protective equipment requirements. Do not use
synthetic wiping rags or cloths with these
materials. Keep CPCs and solvents away from
open flames or sparks.
8-8. PRESERVATION APPLICATION METHODS
.
CPCs can be applied by brushing, dipping, or spraying.
The area of application, viscosity of the material, and
conditions under which they need to be applied are
factors which determine which method of application to
use. Low viscosity (thin) materials are best applied by
spraying, whereas high viscosity (thick) materials are
more suited for brushing or dipping. Dipping can be
used for all types of materials, but the thickness of the
coating obtained with low viscosity materials may be too
thin to provide adequate corrosion protection. Prior to
application of preservatives, remove old preservative
coatings, then apply using one of the following methods.
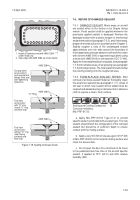
8-8.1. BRUSHING. Brushing may be accomplished
using an ordinary paint brush. This method is most
appropriate for applying thick materials, for use on small
areas, or where it is necessary to prevent material from
getting on surrounding areas or nearby equipment.
8-8.2. DIPPING. Dipping may be accomplished using
any suitable container for the CPC. It is most suitable for
smaller disassembled parts. It cannot be used for
assemblies which contain any part or area adversely
affected by the CPC.
CAUTION
For spray application, do not thin or dilute bulk
preservative unless absolutely necessary. Do
not use synthetic wiping cloths. Mask off
adjacent areas to prevent overspray.
8-8.3. SPRAYING. Spraying may be accomplished
using paint spraying equipment, various types of trigger
sprayers, or aerosol containers. This method is very
effective for application to large areas and where
confinement is not a problem. The viscosity of the
material will determine which type of spraying equipment
to use.
Back to Top