TM-1-1500-344-23-2 - Page 95 of 240
4-19
NAVAIR 01-1A-509-2
TM 1-1500-344-23-2
15 April 2009
(2)
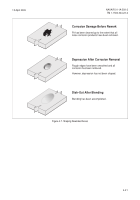
Examine all corroded areas for corrosion
blisters. If intergranular exfoliation is present, use other
recommended mechanical removal methods.
(3)
Blasting shall not be performed on surfaces
where there is a danger of warping or distorting the base
material. Sheet metal, 0.0625 inch (16 gage, U.S.
Standard) or thinner, shall not be blasted without
engineering approval. See the applicable aircraft
manuals for limits on metal removal for the particular
part.
b. Determine what areas should be protected from
the blast stream and from entrapment of the media, and
take action to mask or seal these areas. Composite
surfaces and those requiring a high gloss surface finish
must be effectively protected from the blast. Use impact
resistant PMB tape (3M No. 500 or Intertape BT-100).
c. Static ground the blaster and equipment to be
blasted.
d. Blast corroded areas using the pressures and
materials given in Table 4-4. Do not attempt to use
pressures higher than those specified, since higher air
pressures tend to smear the metal and entrap corrosion
products. When cleaning nonferrous (e.g. aluminum,
magnesium) alloys, never use media which has been
used for cleaning ferrous metals. Abrasives used for
cleaning ferrous metals will contain many particles of
metal which will remain in the abrasive and will
contaminate any nonferrous metal being cleaned. Refer
to applicable abrasive blasting equipment instructions.
(1)
Direct the blast stream at an angle to sweep
across the surface being cleaned (30-40 degrees from
the surface). Several short passes over the corroded
area with the blast nozzle are more effective than one
sustained effort. The passes should start a few inches
before and end a few inches beyond the area to be
cleaned.
(2)
Maintain the nozzle distance from the surface
being cleaned wherever the best cleaning is obtained.
The normal nozzle distance range is from two to six
inches.
(3)
Continue blasting with short passes over the
corroded area to be cleaned until a near-white blast
cleaned surface is obtained. A near-white blast cleaned
finish is a surface finish from which all oil, grease, dirt,
mill scale, rust, corrosion products, oxides, paint, or
other foreign matter have been removed.
WARNING
Use extreme care to ensure that blast media
does not contaminate hydraulic, fuel, oil, coolant,
or oxygen systems. Blockages in flight critical
components caused by abrasive media particles
can result in loss of life and aircraft.
4-10.4.1.1. Operators shall be adequately protected
with complete face and head covering equipment, and
provided with pure breathing air meeting the
requirements of AFOSH Standard 161-1 and NAVOSH
Standard A1-NAVOSH-SAF-000/P-5100-1 when
blasting in confined areas.
4-10.4.1.2.
Finely divided dry particles of many
materials (metallic, organic, and inorganic) can form
explosive mixtures with air. In dust form, certain metallic
materials, notably titanium and magnesium, are capable
of igniting spontaneously when exposed to air. Due to
potential fire and explosion hazards, one should be
careful with these materials when dry abrasive blasting.
4-10.4.1.3. Dry abrasive blasting of titanium alloys
and high strength steel creates sparking. Take care to
ensure that there is no hazardous concentration of
flammable vapors present.
4-10.4.1.4.
After blasting in confined areas, it is
essential that all blasting media and other residue be
completely removed. The blasting media can be very
slippery and can cause dangerous falls.
4-10.4.2.
Abrasive Blasting Procedures. The blasting
operation should be accomplished in the following steps:
CAUTION
When blasting aluminum alloys or magnesium
alloys, do not allow the blast stream to dwell on
the same spot longer than 15 seconds. Longer
dwell times will cause excessive metal removal.
a. Inspect areas and surfaces to be blasted and
decide what techniques will be used. Clean oil and
grease from surfaces with diluted MIL-PRF-85570 Type
II or an approved cleaning solvent (e.g. MIL-PRF-680
Type II or MIL-PRF-32295 Type I).
(1)
Blasting shall not be used in areas or under
conditions that would allow any escaped abrasive
particles to contaminate any system, engine, or other
component.
Change 1 - 31 March 2010
Back to Top