TM-9-2815-205-24 - Page 836 of 856
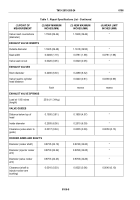
GLOSSARY - Continued
Term
Definition
Leakage
Evidence of a fluid beyond its container
Meniscus
The lowest point of a fluid in a narrow container
Multimeter
A general purpose electrical meter used to measure amperage, voltage, and
resistance.
Nick
A small groove or notch. Usually, displacement of material rather than loss.
Overheating
A condition indicated by discoloration of parts which usually results in a loss
of hardness. Usually caused by a lack of lubrication, malfunction of parts, or
excessive wear.
Parent Metal
Original machined or cast metal form or shape/Base metal
Peen
To deform metal caused by pounding with a hard object.
Pitting
A material surface cavity, usually with defined rough edges. Usually caused
by rust and corrosion.
Radial
Going from the center outward or from the circumference inward along a
radius. A circular direction at a specific radius.
Repair
A process of fixing something that is damaged or worn or does not operate
or function properly.
Rub
Evidence of friction caused by contact of two items.
Runout
The different surface level of a machined surface when a part is turned
axially.
Scoring
Deep tears or breaks in material surfaces from foreign contact under
pressure. May show temperature effect from high friction.
Scratch
A slight tear or break in material surface from momentary foreign contact.
Spline
A keyway between two mating parts. Usually used with multiple keyways.
Teflon
Synthetic fluorine-containing resins (polytetrafluoroethylene) used for
molding articles and for coatings to prevent sticking.
Uneven Wear
Excessive wear in local areas. Includes hollows, shiny spots, uneven polish,
and abrasions of parts subject to fluid, air, or gas flow.
Wear
Loss of material from contacting surfaces. Normal wear is the slow loss of
material from contacting surfaces. Wear usually has a polished finish and
leaves a pronounced pattern.
TM 9-2815-205-24
Glossary-2
Back to Top