TM-1-1500-344-23-2 - Page 78 of 240
4-2
NAVAIR 01-1A-509-2
TM 1-1500-344-23-2
15 April 2009
WARNING
Primers and paints may contain toxic materials
such as chromates and lead. Use eye protection,
gloves, and cartridge respirator during
mechanical paint removing operations. Contact
the local safety and health office for proper
personal protection equipment (PPE).
4-5.1. ABRASIVE MATS, FLAP WHEELS AND
BRUSHES. See paragraph 4-9 for a complete
description of authorized materials, equipment, and
procedures.
4-5.1.1. Composite Surfaces. Use medium grade
(Grade C) abrasive mat (A-A-58054) for scuff sanding.
The abrasive mat may be wet with fresh water or diluted
cleaning compound (MIL-PRF-85570) to prevent
clogging. See paragraph 4-4.1.1 for removal limits.
4-5.1.2. Metal Surfaces. Use a fine (Grade B) or very
fine (Grade A) abrasive mat on an orbital sander, or fine
or very fine flap brushes on a pneumatic drill, for scuff
sanding.
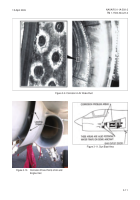
4-5.1.3. Cadmium Plated Steel Surfaces. Sanding to
smooth or remove paint from cadmium plated high
strength steel components shall be done with great care
to avoid penetrating the cadmium, which can be
extremely thin. If unprotected, high strength steel aircraft
parts can experience detrimental levels of corrosion
within just a few hours. Hand sand with 240 grit or finer
abrasive paper or cloth until the primer coat is reached,
then switch to 400 grit or finer paper or cloth.
CAUTION
Radial bristle discs are authorized for use only
on aluminum, magnesium, high-strength steel,
and titanium surfaces as a replacement/
substitute for abrasive wheels and brushes
cited in this chapter. Use of the discs on other
metallic or composite surfaces is not authorized
and may result in damage to the surface or
structure.
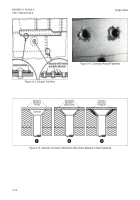
4-5.2. 3M™ RADIAL BRISTLE DISC. The 3M™ radial
bristle disc has been proven to be effective and less
aggressive than abrasive wheels and brushes and is
intended for spot paint removal. The 400 grit (orange)
disc may be used for spot paint removal and will leave
IVD aluminum or cadmium plating mostly intact on high-
strength steel surfaces. Refer to paragraph 4-9.2.1 for
operating instructions.
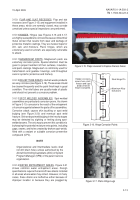
4-5.3. PORTABLE VACUUM SANDING SYSTEMS.
Air quality regulations mandate containment of airborne
particulates from sanding and grinding operations on
metallic and composite surfaces. Vacuum sanding
systems are suction-type equipment used for collecting
paint, metal, and carbon/epoxy dust from grinding and
sanding operations. If appropriate filters (e.g. activated
carbon) are used, then vapor, mist, gases, fumes, and
odors can also be captured. Because the systems are
portable, they allow for work to be done on location
rather than in a booth. These compact, self-contained
units are equipped with sanders, abrasives, adjustment
tools, air supply and vacuum hoses, vacuum hose
connectors, supply air hose fittings and a high efficiency
filter vacuum system for dustless sanding.
CAUTION
Abrasive blasting using glass beads or
aluminum oxide shall not be used for removing
paint. Glass bead and aluminum oxide blasting
may be damaging to the underlying metal.
4-5.4. PLASTIC MEDIA BLASTING (PMB). PMB is an
abrasive blasting method used to remove paint coatings
on metal surfaces. PMB is a quick and environmentally
preferred alternative to most types of chemical paint
removers, but it can cause damage to underlying metal
and injury to personnel if not performed by trained
operators using approved methods. PMB of Army aircraft
components and parts shall be performed using the
requirements and controls in Appendix B, Section VII.
4-5.4.1. PMB Training. Prior to using any PMB
equipment, operators shall receive specialized
on-the-job training conducted by qualified operators.
Operators with limited training or who are newly trained
shall only perform PMB processes under the direct
supervision of properly trained personnel.
a. Training shall include familiarization with the
specific equipment manufacturer’s operating and
maintenance manuals, and the guidelines and
parameters as outlined in this chapter.
b. Training shall also include lectures and
demonstrations on equipment operation and
maintenance, masking and blasting techniques, process
parameters, damage recognition, media contamination
prevention and removal, and safety requirements.
c. Training shall be documented in accordance with
local requirements.
Back to Top