TM-9-2910-226-34 - Page 43 of 208
TM 9-2910-226-34
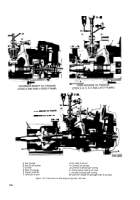
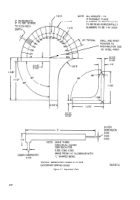
Table 2-1. Special Tools
Section Il. TROUBLESHOOTING
2-6. Purpose.
a.
Information
use of maintenance personnel
in this section is for
in conjunction with,
and as a supplement to the troubleshooting sections
in the pertinent
vehicle and engine technical
manuals. It provides continuation of instructions
where a remedy in the above technical manuals refers
to maintenance personnel for corrective action.
b.
Operation of a deadlined vehicle without a
preliminary examination can cause further damage
to a disabled fuel injection pump and possible injury
to personnel.
By careful inspection and
troubleshooting, such damage and injury can be
avoided and, in addition,
the cause of faulty
operation of a vehicle or fuel injection pump can
often be determined without extensive disassembly.
2-7. General Instructions and Procedure.
This
section contains inspection and troubleshooting
procedures to be performed after a fuel injection
pump has been removed from the vehicle and/or
power plant.
a.
Inspection after the fuel injection pump is
removed from the vehicle and/or engine is performed
to verify any diagnosis made when the pump was in
the vehicle,
to uncover further defects, or to
determine any malfunction if the component alone is
received by the maintenance activity. This in-
spection is particularly important in the last case
because it is often the onlv means of determining the
.
malfunction without disassembling the fuel injection
pump.
b.
Troubleshooting a disabled fuel injection
pump after it has been removed from the vehicle
and/or engine consists of subjecting it co tests on a
suitable test stand. This section discusses those
symptoms which can be diagnosed by using the
testing equipment and interprets the results in terms
of probable causes. Information pertaining to this
test is contained in paragraphs 3-49 through 3-52.
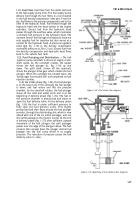
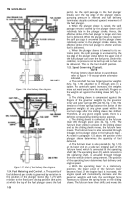
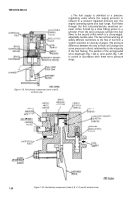
2-8. Procedures.
After a metering and distributing
fuel injection pump has been received by the
maintenance activity for preliminary inspect ion, or if
performance of the pump has been unsatisfactory
due to unknown causes, it must be checked before
installing it on a test stand. This check should in-
clude a search for any binding or broken parts by
rotating camshaft and operating lever. When cause
for failure has been found, fuel injection pump
should be disassembled and repaired
before
proceeding with the tests. Additional operational
tests performed on a damaged fuel injection pump
could only increase the damage. If no cause for
failure is found in inspection, fuel injection pump
should be put on test stand and troubleshooting
performed.
2-3
Back to Top