TM-9-2320-361-24-1 - Page 206 of 1176
MALFUNCTION
TEST OR INSPECTION
CORRECTIVE ACTION
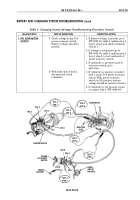
1. NO ALTERNATOR
OUTPUT
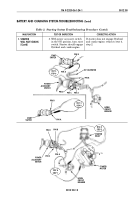
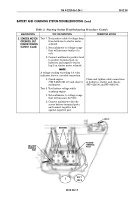
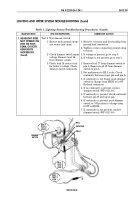
5. Measure voltage at terminal
end of lead 568.
Test 4. Test positive output of
alternator.
NOTE
• Access cover was removed in test 3.
• Input amps decrease in input
voltage normally causes an increase
in alternator output voltage.
1. Start engine
(TM 9-2320-361-10).
2. Set engine speed at 1200 RPM.
3. Turn headlights and
accessories to ON position.
4. Use multimeter to measure
alternator output voltage at
positive terminal (lead 2).
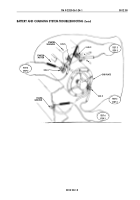
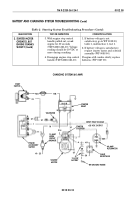
Test 5. Test voltage drop on lead 2.
Place multimeter positive lead
on alternator positive output.
Place multimeter negative
lead on starter solenoid lug 2.
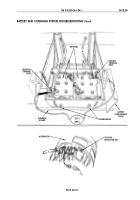
Test 6. Test battery voltage into
power accessory switch
(WP 0012 00, table 3,
malfunction 1, test 4).
1. Disconnect lead 1 from pin D
of power accessory switch.
2. Turn power accessory switch
to ON position.
1. If battery voltage is present
(normal), the alternator is
defective. Go to test 4 and check
positive output of alternator.
2. If voltage is not present, an open
lead or bad connection exists in
lead 568. Repair or replace lead
(WP 0090 00). Return to test 2.
1. If output voltage is between 24.0
and 26.0 VDC, replace alternator
(WP 0085 00).
2. If output voltage is more than
28.5 VDC, go to test 5 and check
voltage drop on lead 2.
1. If voltage drop on lead 2 is greater
than 0.4 volts, repair or replace
lead (WP 0090 00). Go to test 2.
2. If voltage drop on lead 2 is less
than 0.4 volts (normal), voltage
regulator output is too high.
Replace alternator (WP 0085 00).
TM 9-2320-361-24-1
0012 00
0012 00-22
BATTERY AND CHARGING SYSTEM TROUBLESHOOTING (Contd)
Table 3. Charging System (60 Amp) Troubleshooting Procedure (Contd).
Back to Top