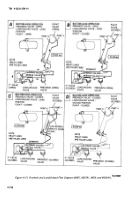
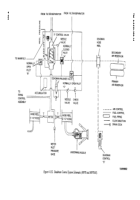
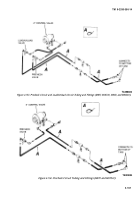
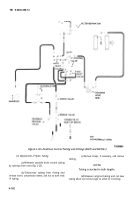
TM-9-2330-356-14
SEMITRAILER, TANK: 5000 GALLON, BULK HAUL, SELF LOAD/UNLOAD M967 AND M967A1; SEMITRAILER, TANK: 5000 GALLON, FUEL DISPENSING, AUTOMOTIVE M969 AND M969A1; SEMITRAILER, TANK: 5000 GALLON, FUEL DISPENSING, UNDER/OVERWING AIRCRAFT M970 AND M970A1
TECHNICAL MANUAL; OPERATOR’S, UNIT, DIRECT SUPPORT, AND GENERAL SUPPORT MAINTENANCE MANUAL
OCTOBER 1990
TM-9-2330-356-14 - Page 304 of 528
TM 9-2330-356-14
d.
Use cotton waste for cleaning
material may generate static electricity.
e.
Required Materials.
purposes; other
(1) Adequate source of water with a large
diameter hose long enough to reach the semitrailer.
(2) Compressed air source and air hoses of
sufficient length to reach bottom of semitrailer tank.
(3) Sufficient quantity of gas tank purger
chemical obtainable through local procurement. Purging
chemical No 913, Product-Sol Inc., 2010 Cole Avenue,
Birmingham, Michigan 48008 is the only known source
available to date. Purging chemical can be procured at a
cost of approximately $70.00 per 5 gallons, or $420.00 per
55 gallons, plus shipping cost.
(4) Combustible gas indicator set (NSN 6665-00-
664-4650 or NSN 6665-00-292-9945). The equipment is
listed as a Common Table of Allowance (CTA) item in SB
700-20 and is line item number E57351.
(5) Entry into a tank which is not vapor-free or
which has an oxygen content less than 19.5% require the
following: Protective respiratory equipment; lifeline;
approved explosion-proof extension light or flashlight;
steam or air-operated venturi-type air mover or a fan-type
blower with an air duct.
f.
Purging-Chemical Method.
(1) After draining tank, close or seal all valves
and drain points.
(2) Fill tank with cold water and allow to
overflow for five minutes or until all traces of flammable
material are removed. Drain tank completely.
(3) Close or seal all valves and drain points.
CAUTION
Insufficient amount of chemical will result In
an incomplete purging. Once purging has
begun, do not stop until process Is complete.
(4) Add to tank 40-fluid ounces of the
chloro-carbon base purging chemical for each 100-gallon
capacity. A 5000 gallon tank will take approximately
17 gallons of purging chemical.
(5) Fill tank to top with water. Do not overflow.
(6) Insert air line through manhole and vent cap
openings and agitate solution with 3-5 psi of air for
40 minutes. Frequently move air hoses around in tank,
covering as much area as possible, especially near the
bottom and around baffles. Remove air lines and drain
solution from tank at all valves and drain points.
(7) Fill tank with cold water and allow to
overflow for 5 minutes or until water is clear. Drain tank
completely at all valves and drain points.
(8) Conduct a combustible vapor test to
determine if tank is safe to repair, clean, paint, store,
change material, or ship. Take reading in several areas of
the tank. If test reading indicates tank is not safe, repeat
step (7), until a safe reading is obtained.
g.
Purging–Steam Method.
(1) This methods is an alternate to the chemical
method, It is effective for the removal of high viscosity
petroleum products. Low pressure steam is injected into
the tank for a period of time to bring the temperature of
the tank to 76°C (170°F). Prior to introducing steam, the
metallic connection on the discharge end of the steam
hose must be bonded to the tank shell and the tank must
be grounded.
(2) After draining tank, ensure that all valves and
drain points remain open.
(3) Introduce steam through manhole and baffle
plate opening in sufficient volume to raise the
temperature of the tank to 76°C (170°F). Close manhole
fill cover to the extent steam line will permit.
CAUTION
Ensure that steam does not come in contact
with electrical wiring and other components.
The heat of steam can damage the painted
surface of the tar, valve seats, gaskets, and
diaphragms, and can weaken fusible plugs.
(4) Steam the tank for at least three hours. Turn
steam source off.
CAUTION
After purging by steam method, leave tank
valves and drain points open during
cool-down to prevent vacuum collapse of
tank.
(5) Leave an valves and drain points open until
tank is fully cooled, at least one hour.
(6) Measure explosive vapor level. Take readings
in several areas of the tank. Reading should be 20% lower
explosive level (LEL) or less. If LEL is greater than 20%,
4-168
Back to Top