TM-9-2320-279-20-1 - Page 352 of 985
TM 9-2320-279 -20-1
STE/lCE Instructions (Cent)
2-16. SIMPLIFIED TEST EQUIPMENT FOR INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES (STE/lCE)
INTRODUCTION (CONT).
●
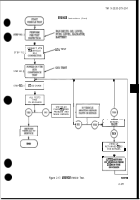
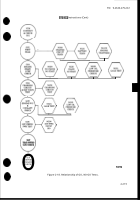
(3) Isolation and Correction of Specific Malfunctions. When
a specific malfunction is known,
unnecessary testing can be avoided by going directly to the appropriate test, or tests, indexed in ‘Ihble 2-10
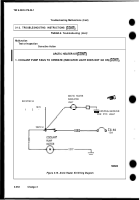
or 2-11. The relationship of the GO and NO-GO tests are shown in Figure 2-18. Note that GO1 test, VTM
connections and checkout, must be performed before conducting any other tests.
c.
SWICE Operation and Description.
STE/ICE is a testing system that performs tests and
measurements on internal combustion engines. STE/ICE measures standard voltage, current, resistance,
pressure, and temperature. Special tests, such as compression balance tests and starter system evaluations
are performed by STE/ICE. Standard equipment functions including vacuum pressure gage, low-current
tester, and multimeter are features of the STE/ICE set. STE/ICE is portable and operates on either 12 or
24-volt vehicle batteries or equivalent power source. The STE/ICE system consists of a Vehicle Wst Meter
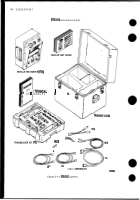
(VTM), a Transducer Kit (TK), four electrical cables, a transit case, and technical manual (fig. 2-19).
d. Vehicle Test Meter
(VTM).
(1)
VTM Description.
The VTM is a tool for the mechanic to test vehicle electrical and mechanical
components. Readings are either pass/fail indications or digital displays in units familiar to the mechanic
(psi, rpm, volts, ohms, amps, etc.).
(2’)
VTiWInterfaces.
The VTM interfaces with the vehicle by either a permanently mounted
Diagnostic Connector Assembly (DCA) or directly with a transducer from the Transducer Kit (TK). The
DCA provides accessibility to the most frequently needed test points. This use of the VTM is called the
DCA mode of operation. The VTM also interfaces with transducers from the transducer kit for testing or
troubleshooting. This use of the VTM is called the TK mode of operation. Additional tests not in the DCA
mode can also be done in the Transducer Kit (TK) mode. These involve manually probing and/or connecting
transducers to appropriate test points.
(3)
VTMPowe~
Operating power for the VTM is drawn from the vehicle batteries or some equivalent
battery source. Power is routed to the VTM through the diagnostic connector in the DCA mode, or through
cable clamps connected to the battery in the TK
mode.
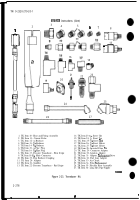
e. Transducer Kit Components.
The Transducer Kit contains a pulse tachometer transducer, a
—
pressure and a vacuum transducer along with the necessary adapters (bushings, plugs, tees, etc.). Also
included in the kit is a current probe for measuring current and a test probe cable for measuring voltage
and resistance. The transducers and adapters are non-repairable. The cables are non-repairable at
organizational maintenance level.
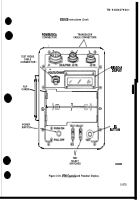
f. Vehicle Test Meter (VTM) Controls and Readout Display.
The controls and readout display
on the VTM are illustrated in Figure 2-20. The following paragraphs describe how the controls are used,
and how the display functions.
(1) Power Switch (PUSH ON/PULL OFF).
The power switch controls DC power to the VTM. The VTM
can operate from a 12-volt or 24-volt battery system. When the power switch is pushed in (PUSH ON), the
VTM power is on. ‘lb shut the VTM off, pull out the power switch (PULL OFF). The power switch contains
a 4-amp circuit breaker. The power switch will pop out automatically if something is wrong which causes
the VTM to use more power than it should. If the switch pops, check the hookup carefully and try again
before sending the VTM to DS Maintenance.
2-272
Back to Top