TM-5-3805-254-14-P-2 - Page 345 of 894
TRUCK SERVICE MANUAL
ENGINE
a.
Hold ring in groove, flush with land and insert 0.006
inch [0.15 mm] feeler gauge.
b.
If gauge enters groove without forcing or disengaging
ring, wear is excessive and piston should not be used.
3.
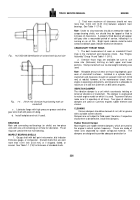
Measure piston skirt diameter with micrometer at right
angle to piston pin bore (A, Fig. 1-11 for barrelground pistons);
measure straight or tapered ground pistons at Point B, 1 inch
[25.4 mm] below ring groove and C, 1 inch [25.4 mm] above
bottom of piston.
Pistons should not be reused if worn more
than 5.483 inch [139.27 mm].
a.
Pin Bore Area
b.
Area Below Ring Groove
c.
Piston Skirt
Fig.
1-11 (N20171) Piston check points.
4.
Pistons should be checked at temperature of 70 to 90
deg. F [21 to 32 deg. C].
After measuring piston and
comparing
with
liner
inside diameter,
piston-to-liner
clearance may be computed if desired.
5.
Piston pin bore checked at 70 deg.
F [21.1 deg. C]
should fall within limits shown in Table 1-1; add 0.0005 inch
[0.013 mm] per 10 deg. F [-12 deg. C] up to 90 deg. F [32 deg.
C] .
6.
Check piston pin outside diameter with micrometer.
Pins should not be reused if out-of-round more than 0.001 inch
[0.03 mm] or worn smaller than indicated in Table 1-1 (13).
Reboring of piston pin bores and use of oversize pins is not
practical because the misalignment that results from such
practice will cause seizure of piston or failure of connecting rod
bearings.
Piston-To-Connecting Rod Assembly
1.
Pistons are machined to a very close weight tolerance;
therefore, as long as the same part number piston is used
throughout the engine, weight does not affect engine
operation.
2.
Be sure rod and cap are stamped with cylinder number
from which removed before disassembly to prevent mixing
parts.
3.
Install one piston pin snap ring in groove of piston pin
bore.
4.
Heat aluminum pistons in boiling water or in an oven at
or below 210 deg. F [98.9 deg. C] and install pin through
piston and connecting rod pin bores before piston cools; at 70
deg. F [21 deg. C] the pin fit is 0.0001 to -0.0003 inch [0.003 to
-0.008 mm] which prevents pin assembly unless piston is
heated, Secure pin with second snap ring in groove at
opposite end of pin bore.
CAUTION
Never drive piston pin in pistons.
Driving may cause
distortion of piston, causing piston seizure in cylinder
liner.
REAR COVER
The rear cover is a unit subject to replacement of seals only.
Damaged housings require replacement by a new assembly or
installation of a "Heli-Coil" for stripped threads; these are only
items of repair.
Alignment during engine assembly is the biggest factor for
proper performance of the rear cover unit.
See Group 14.
CAMSHAFT
INSPECTION
Check
camshaft
bushing
journals
with
micrometers.
Replace camshaft if journals are worn beyond limits given in
Table 1-1 (15).
Replace camshafts that have scuffed, scored, or cracked
injector or valve lobes.
Check by magnetic inspection for
possible cracks.
Cummins Engine Company, Inc.
does
not
recommend
regrinding of camshaft lobes.
Camshaft Support
If cast iron support is used, inspect bushing in support;
remove if damaged or worn smaller than 1. inch [34.80 mm];
press in new bushing flush with inner bore.
New dimensions
are 1.3725 to 1.3755 inch [34.86 to 34.93 mm].
Replace
aluminum support.
Thrust Bearing
Inspect thrust bearing for flaking, burrs, distortion and
341
Back to Top