TM-9-2330-356-14
SEMITRAILER, TANK: 5000 GALLON, BULK HAUL, SELF LOAD/UNLOAD M967 AND M967A1; SEMITRAILER, TANK: 5000 GALLON, FUEL DISPENSING, AUTOMOTIVE M969 AND M969A1; SEMITRAILER, TANK: 5000 GALLON, FUEL DISPENSING, UNDER/OVERWING AIRCRAFT M970 AND M970A1
TECHNICAL MANUAL; OPERATOR’S, UNIT, DIRECT SUPPORT, AND GENERAL SUPPORT MAINTENANCE MANUAL
OCTOBER 1990
TM-9-2330-356-14 - Page 426 of 528
TM 9-2330-356-14
b.
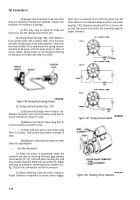
Remove air intake manifold (para 4-82).
7-90. Starter Tests
c.
Remove four fuel injectors (para 7-28).
d.
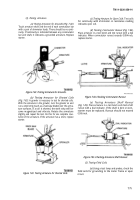
Insert a compression gage and adapter (table 5-1
and fig. 7-25) into the Number 1 cylinder fuel injector
opening in the cylinder head. Secure the adapter to the
cylinder head with two 5/16-18 NC x 3/4 capscrews.
NOTE
The best indication of compression leakage
is the pressure difference between cylinders.
Compression of a standard new engine
cranking at about 300 rpm is approximately
350-400 psi.
Maintenance should be
considered If pressure is below 325 psi or If
there Is a 15% or more difference between
cylinders.
e.
Turn the engine START switch to the start
position to crank the engine. Record the compression
reading on the gage as the engine is being cranked.
f.
Remove the compression gage and adapter.
Insert adapter in Number 2 cylinder fuel injector opening.
Secure with two capscrews.
g.
Turn the engine START switch to the start
position and crank engine. Record the compression
reading on the gage as the engine is being cranked.
h.
Repeat steps
f
and
g
for Number 3 and Number 4
cylinders.
i.
Install fuel injectors (para 7-46).
j.
Install air intake manifold (para 4-82).
k.
Replace shroud door panel.
a.
On Equipment Test.
Refer to paragraph 4-79 for on
equipment test.
b.
Bench Tests.
(1)
Testing Starter.
(a)
If starting motor tests are required,
remove the motor from the engine and test it on a bench.
Test the free-running voltage and current.
(b)
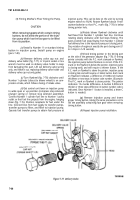
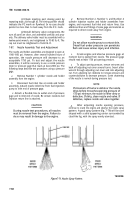
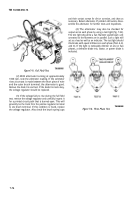
Using a spring scale and torque arm, test
the stall torque (Fig. 7-81). Multiply the spring scale
reading by the arm length for the torque value.
(c)
If free running speed is low, and starter
has a high current draw with low stall torque, check for
tight, dirty or worn bushings, bent armature shaft, or loose
field pole screws, allowing armature to drag. Check also
for shorted or grounded armature and field.
(d)
A low free speed with low torque and
low current draw indicates an open field winding, high
internal resistance due to poor connections defective
leads, broken or worn brushes, or scored, worn, or dirty
commutator.
(e)
High free speed with low developed
torque and high current draw indicates shorted fields.
Since there is no easy way to detect shorted field coils,
replace and check for improved performance.
(f)
The voltage drop across the solenoid on
the starting motor should be less than 1.5 volts. If not,
remove it for repair.
Figure 7-81. Testing Stall Torque.
7-70
Back to Top