TM-9-1200-215-34-P - Page 160 of 266
TM 9–1200–215–34&P
6–6
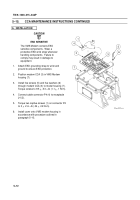
The PWM is controlled by two voltage comparators. The first voltage comparator monitors the vehicle voltage
level. If this level is below 20 volts the PWM is enabled and the output of the PCU is supported by the voltage
doubler.
The second voltage comparator monitors the voltage drop across a current sense resistor that is connected
between the source of the MOSFETs and vehicle return. If the voltage drop across the sense resistor exceeds a
predetermined level the PWM will be powered down. This only occurs if the system is demanding too much
power to be safely delivered from the PCU or a short has occurred in the PCU. This is a pulse by pulse current
limiting technique and will only power down the PWM as long as the overcurrent situation continues.
2
=
OUT
OUTPUT
FILTER
A
B
CR1
CR2
TRANSFORMER
2
2V
–
+
+
–
V
R
IN
IN
FET
BANK A
FET
BANK B
DRIVE
IN
TO
SYSTEM
=
OUT
IN
CURRENT
SENSE
IN
PWM
CONTROLLER
V
I
I
I
I
Figure 6–3. Voltage Doubler Block Diagram
The output voltage of the doubler, due to the resistance of the interconnections and losses in the transformer and
diodes will not exactly be double the input voltage but will support the AFCS.
(7)
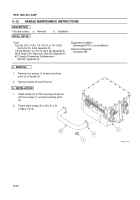
Back–up battery charger. The back–up batteries are charged by the PCU. The back–up battery charger
in the PCU is a DC to DC converter. The back–up battery charger block diagram is shown in figure 6–4.
Figure 6–4. Back–up Battery Charger Block Diagram
CR1
CR2
+
LR
+28V
C
FROM
VEHICLE
V
–
IN
RTN
INPUT
FILTER
GATE DRIVE
CURRENT
SENSE
PWM
CONTROLLER
TEMPERATURE SENSE
OUTPUT
VOLAGE
SENSE
TO BACKUP
BATTERY
ASSEMBLY
OUT
TO THERMISTOR
IN BACKUP
BATTERY
ASSEMBLY
FETS
V
OUT
+
–
INPUT VOLTAGE SENSE
I
Back to Top